
Positive and negative integers can be shown on a number line. Positive integersNegative integers We can use the number line to compare integers. For example, –3–8 –3 ‘is greater than’ –8 Integers on a number line
Positive and Negative numbers
For example, –3 is an integer. This can also be written as – 3. It is 3 less than 0. 0 – 3 =–3 Here the ‘–’ sign means minus 3 or subtract 3. Here the ‘–’ sign means negative 3..
Positive integersNegative integers We can use the number line to compare integers. For example, –3–8 –3 ‘is greater than’ –8 Integers on a number line.
–2 + 5 = -23 = 3 To add a positive integer we move forwards up the number line..
5 – 8 == –3 To subtract a positive integer we move backwards down the number line. 5 – 8is the same as5 – +8.
To add a negative integer we move backwards down the number line. –3 + –4 = = – –3 + –4is the same as–3 – 4 Adding integers.
To subtract a negative integer we move forwards up the number line. 3 – –6is the same as3 + 6 Subtracting integers.
–4 – –7 = -43 = 3 To subtract a negative integer we move forwards up the number line. –4 – –7is the same as–4 + 7 Subtracting integers.
To add a negative integer we move backwards down the number line. To subtract a positive integer we move backwards down the number line. To subtract a negative integer we move forwards up the number line. a + – b is the same as a – b. a – – b is the same as a + b..
When we are dividing negative numbers similar rules apply: +×+=+ –+×= – –+×=– –+×=– +÷+=+ –+÷= – –+÷=– –+÷=–.
Multiplying and dividing integers Complete the following: –3 × 8 = 42 ÷ = –6 × –8 = × = –141 –72 ÷ –6 = –36 ÷ = –4 ÷ –90 = –6 –7 × = 175 –4 × –5 × –8 = 3 × –8 ÷ = 1.5 –24 –7 –12 –3– –25 –160 –16
Always make sure that answers given by a calculator are sensible..
Sums and products Start by writing down all of the pairs of numbers that multiply together to make –8. Since –8 is negative, one of the numbers must be positive and one of the numbers must be negative. We can have: –1 × 8 = –81 × –8 = –8–2 × 4 = –8or 2 × –4 = –8 –1 + 8 = 71 + –8 = –7–2 + 4 = 22 + –4 = –2 The two integers are –2 and 4..

Positive and Negative Numbers (examples, solutions, videos, worksheets)
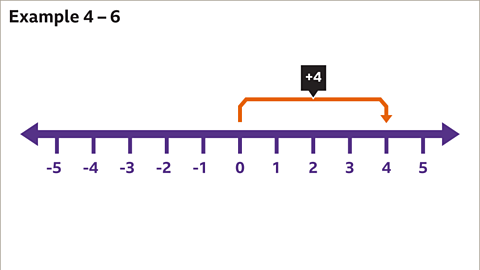
KS3 Maths: How to add and subtract positive and negative numbers - BBC Bitesize

Adding and Subtracting Real Numbers Section 1-5. Goals Goal To find sums and differences of real numbers. Rubric Level 1 – Know the goals. Level 2 – Fully. - ppt download

Positive and Negative numbers. Negative numbers A positive or negative whole number, including zero, is called an integer. For example, –3 is an integer. - ppt download
Using a Number line with Positive and Negative Numbers

PDF) CLASS X (SA ∆ABC ~ ∆ SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT 3 X AG-13 _SA-1_.pdf · Show that cube of any positive integer is of the form 4m or 4m + 1 or 4m +
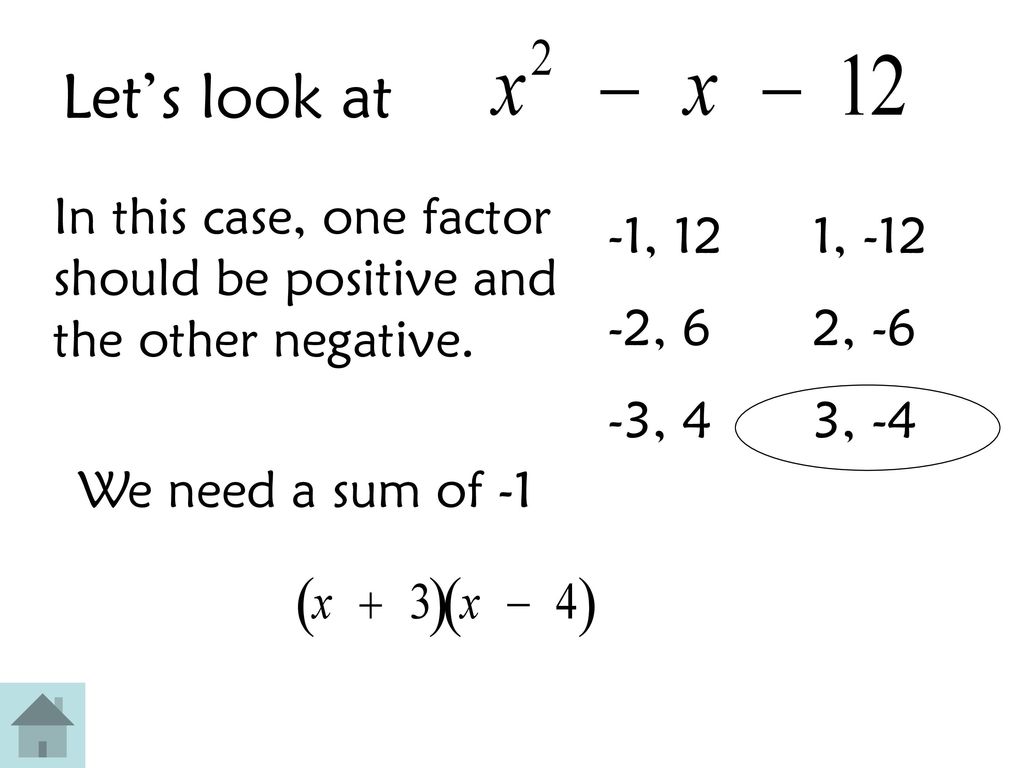
Factoring when a=1 and c > ppt download

Effect of the exchange current density (j 0 ) on the the current density (j): j(t) = j 0 {exp [- nF /RT] - exp[(1- )nF /RT]} - ppt download
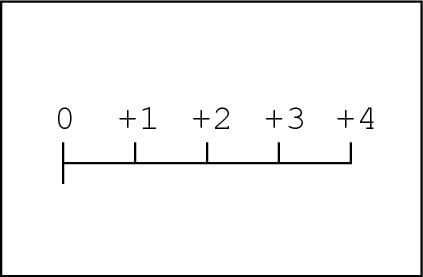
Basics of Positive and Negative Numbers - dummies

Adding Positive and Negative Numbers

Bell Ringer 58, What is the place value of the 8? - ppt download

CALCULATOR MANIPULATION. Due to the differences in calculators you will have to be able to use your own effectively. - ppt download

Adding & Subtracting Positive & Negative Integers - Classroom Math Poster : Office Products

Effect of the exchange current density (j 0 ) on the the current density (j): j(t) = j 0 {exp [- nF /RT] - exp[(1- )nF /RT]} - ppt download






