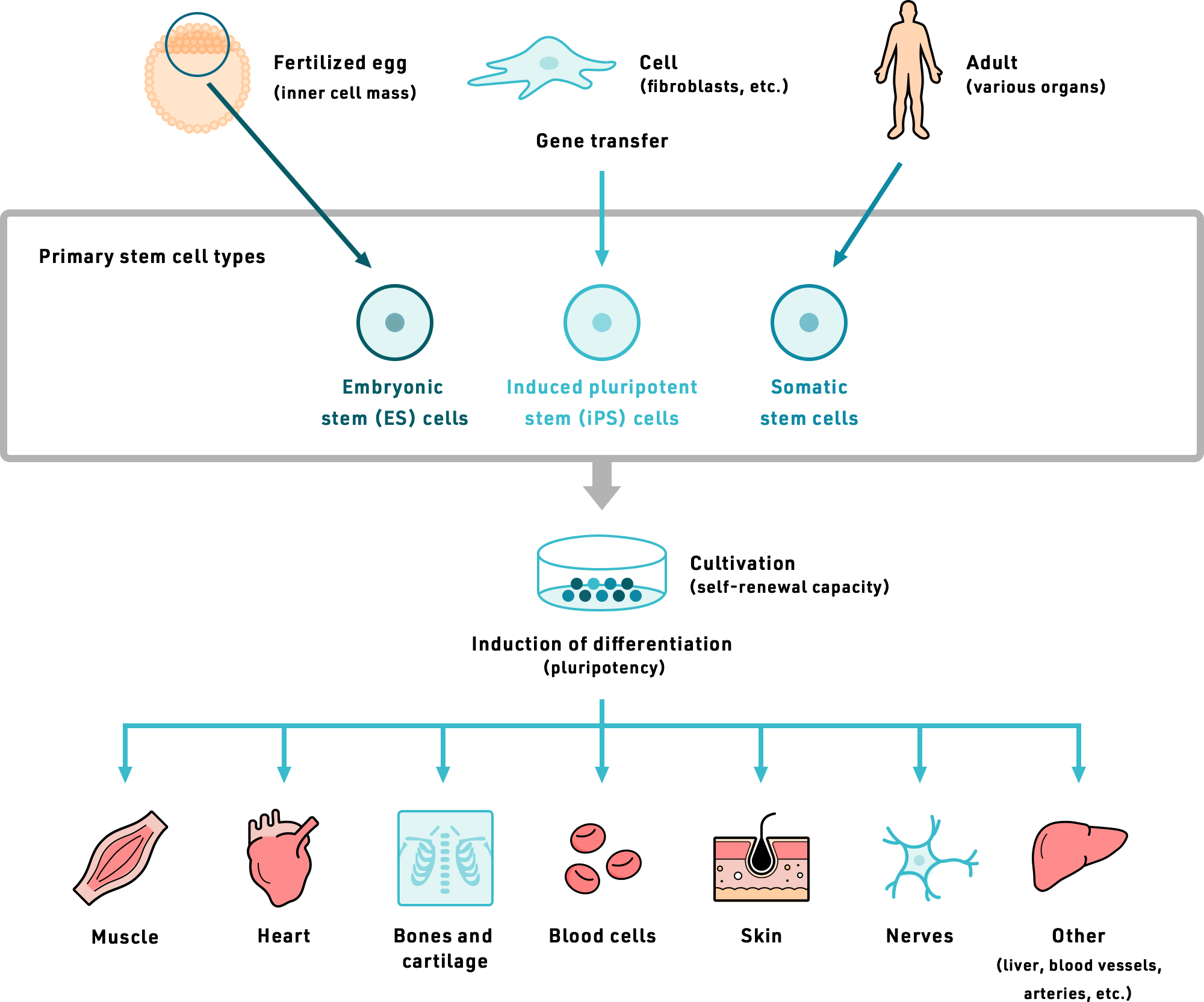
Download scientific diagram | Cellular origin of the de novo formed tissue during organ regeneration in the zebrafish. (A) Dedifferentiation, proliferation and re-differentiation. (Ai) In the heart, cardiomyocytes in close proximity to the injury revert to a less differentiated stage, re-enter the cell cycle and redifferentiate into mature cardiomyocytes. (Aii) During regeneration of minor liver damage, hepatocyte regeneration occurs with no signs of dedifferentiation prior to cell cycle entry and proliferation. (B) Blastema formation as an intermediate step during regeneration. After fin amputation, cells of various lineages -including osteoblastsdedifferentiate and accumulate under an apical epidermal cap. They then proliferate and redifferentiate to rebuild the missing fin structures. (C) Phenotypic switch or transdifferentiation during regeneration. Example: after extensive liver damage, biliary ductal cells (green) can transdifferentiate into hepatocytes (green hexagonal cells) that then differentiate into mature proliferating hepatocytes. (D) Stem cells as progenitor cells. Neural stem cells/progenitor cells proliferate and differentiate into new neurons during regeneration of the central nervous system. While neuronal regeneration has been well described, less information is available on robust axon regrowth. Yellow, differentiated cells; orange, dedifferentiated cells; purple, non-osteoblast cells within the fin; green hexagonal cells, cells undergoing transdifferentiation; blue, stem cells/progenitor cells. Damaged area is shown in gray. from publication: Model systems for regeneration: Zebrafish | Tissue damage can resolve completely through healing and regeneration, or can produce permanent scarring and loss of function. The response to tissue damage varies across tissues and between species. Determining the natural mechanisms behind regeneration in model organisms | Regeneration, Zebrafish and Injury | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.

Brain organoids replicate key events in human brain development
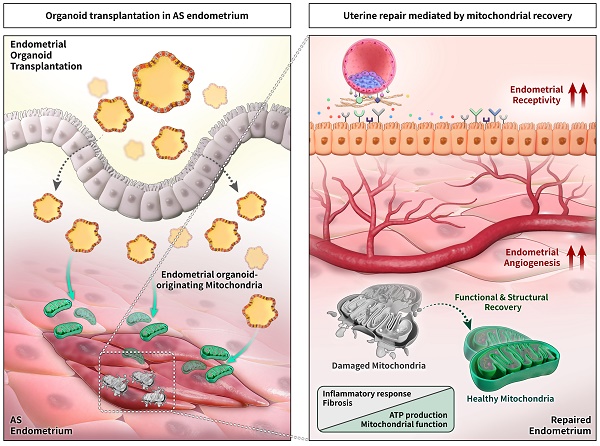
Endometrial organoids: a reservoir of functional mitochondria for uterine repair
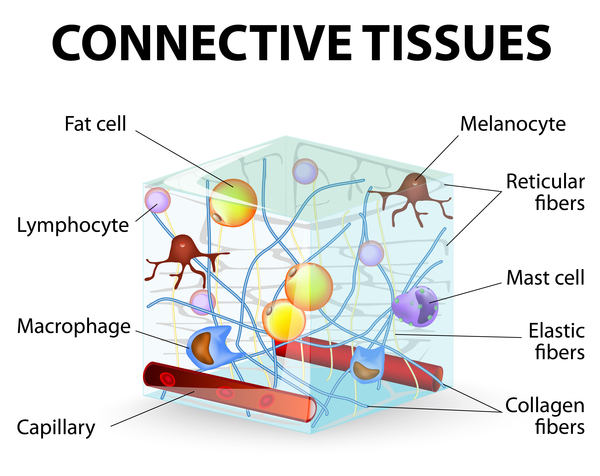
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome: MedlinePlus Genetics

Hatching probability of zebrafish Danio rerio larvae fed different

Representative histologic differences between human and wildtype
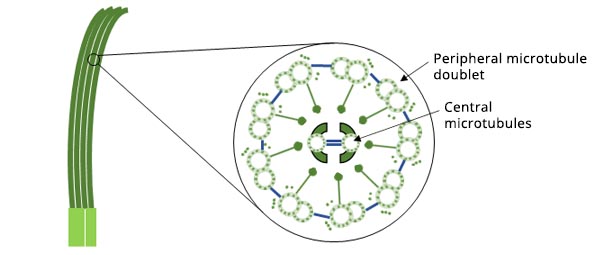
Revealing the Regulatory Mechanisms for the Proper Assembly of Motile Multicilia Using High-Speed Live-Cell Imaging

PPT - Framework PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:1461991

Ines MARQUES, Research Assistant, PhD in Biology, Universität Bern, Bern, UniBe, Institute of Anatomy

PDF] Plant regeneration: cellular origins and molecular mechanisms

Historical Timeline of Tissue Culture - Plant Cell Technology

Nadia MERCADER, Group Leader, Spanish National Centre for Cardiovascular Research, Madrid, CNIC, Department of Cardiovascular Development and Repair (DRC)